Abstract
Financial planning for retirement is essential to ensure that people have enough money to live the lifestyle they desire when they retire. Self-employed business owners in developed countries widely do financial retirement planning. However, in Malaysia, the percentage of self-employed individuals concerned about financial retirement planning is lower than in other countries. This study aims to identify the relationship between the financial attitude, financial literacy and health literacy of self-employed individuals toward sustainable financial retirement planning in Malaysia and find out the moderating effect of the role of financial advisors. The study utilized structural equation modelling. Data were collected through a survey questionnaire and analyzed using SMART PLS 3.3. The total sample size was 416 self-employed individuals from the northern Malaysian region. The findings revealed that financial attitude and financial literacy significantly impact retirement planning. Moreover, the role of financial advisors moderates the relationship between financial attitude–financial retirement planning and financial literacy–financial retirement planning. The result of the study will fulfil the needs of self-employed individuals to plan their retirement by including the financial planning determinants needed for a well-planned retirement.
1. Introduction
Retirement is an important life event that every working individual experiences. After many years in a dedicated job, retirement is when a person exits the workforce. Retirement is the beginning of a new stage of life. Even if people want to work into their later years, age discrimination, mandated retirement, declining productivity, bad health and structural changes in labor compel them to abandon their jobs. According to a report by Hongkong and Shangai Banking Corporation, the four important phases for a well-planned retirement are listed below. Firstly, one should know their retirement requirements while employed. People must know how much they will require to support themselves in retirement. Secondly, priority should be placed on early savings. A certain amount of funds is required to assist the elderly after retirement. Thirdly, people should understand how key life events may affect their finances when preparing for retirement. People with low savings or assets will experience difficulties when faced with unforeseen expenses after retirement. Fourthly, people who want to retire with less debt should be able to make plans. Financial retirement planning is more necessary for people with lower salaries than for those with higher incomes.
Planning is essential in the 21st century since many employees will also need to rely on their savings, unlike past generations of workers who relied solely on pensions. Therefore, one can resolve their money problems through planning. According to Sutherland, financial planning is taking the money you have earned from your work and ensuring you put it to good use in a way that reflects your aspirations and values. Financial planning enables people to examine their financial objectives and take the required actions to update or achieve them. Finally, retiring individuals are urged to seek assistance from financial professionals who can assist them by giving them advice on the important things they should do before they retire.
The Minimum Retirement Age Act 2012 (Act 753) specifies that the minimum retirement age in Malaysia is currently 60. The elderly population in Malaysia is expected to increase steadily from 5.7% in 1990 to 6.3% in 2000 and 9.8% in 2020. According to Nilsson et al., 38% of retirees said they “want to” work until they are 65 years old or older, and 54% of retirees said they still “can” work. One of the main reasons people continue to work after retirement is due to economic issues, including personal wealth and retirement incentives. Children’s education is one of the main reasons Malaysians have greater debt levels.
Studies were conducted in Malaysia to determine the factors influencing elderly labor participation. According to Ling et al., high monthly expenses, particularly for low-income workers, were determined to be one of the contributing reasons to retirees’ labor market participation. They encountered this difficulty because of their lack of financial knowledge. These people need to learn how to prepare their finances for retirement, which can only be done with adequate exposure to financial literacy. According to the Manulife Investor Sentiment Index (MISI) poll, Malaysians lack financial planning even though saving for retirement is their top goal; their current debt-to-income ratio is 68%, the highest ratio among the eight Malaysian markets. Over the past few years, the globalization era has led to higher living standards and longer life expectancies. Due to lower death rates in most countries, the number of people over 60 is increasing daily. Due to societal and economic change, there will be more senior people than children in the future and more elderly workers. When people express their worries about not having enough retirement resources to support rising living expenses and expensive healthcare services in old age, incorrect retirement planning is frequently brought to light in Malaysia. In addition, dependency has increased dramatically from 1975 to 2015. As a result, it is now essential to address concerns relating to retirees and their financial retirement planning. This study aims to determine the variables that affect self-employed Malaysians regarding financial retirement planning. By giving a greater understanding of financial retirement planning and the attempts to preserve their lifestyle after retirement, this research will benefit Malaysians who work for themselves.
The rest of the paper is followed by a literature review, hypotheses development, methodology, findings, analysis, and conclusion.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Planning for retirement is critical to ensure that individuals can have sufficient savings to live the lifestyle they want upon retirement. A single individual firstly does planning. A person with a good personal financial plan may manage their money sensibly. However, it was shown that younger working generations feel burdened by retirement planning because they must make long-term financial plans. In 2019, out of 14.8 million employed persons, 25.08% (3.71 million) were self-employed workers in Malaysia, according to the World Bank’s collection of development indicators. According to the Employees Provident Fund (EPF), 62% of Malaysia’s 22 million working-age citizens work for themselves and are not officially covered by social safety. More than 70% of Malaysians, according to EPF, do not have a rainy-day fund for unexpected needs. Due to poor levels of financial literacy among Malaysians, retirement planning is not well known. To guarantee that people have long-term retirement planning, it is important to encourage retirement planning. According to a preliminary study, successful retirement positively correlates with retirement planning, positive attitudes and success. Previous research underlined the significance of financial retirement planning and examined the factors that impact financial retirement planning. The highlight of being good at planning for retirement is to live a desired lifestyle upon retirement without facing any financial constraints.
The life-cycle saving and investing theory was used to better understand how people make spending and saving decisions based on their life expectancy, income, retirement objectives and intergenerational transfer motives. This is the most prevalent argument because there is a need for basic financial literacy to make effective financial planning decisions, as individuals are expected to take increasing responsibility for their financial affairs. The life-cycle hypothesis investigates workers’ retirement and savings patterns. Because the life-cycle theory implies that individuals aim to maximize the utility derived from their entire life-cycle consumption, consumption must be continuous despite income discontinuities, and saving is needed to finance consumption after retirement. The life cycle hypothesis (LCH) emphasizes maximizing utility across one’s lifetime. As a result, it is anticipated that working people will save money while earning it to be spent in retirement.
2.1. Financial Attitude
Financial attitudes encompass a person’s values and opinions about various personal financial topics, such as whether they think saving money is important. Both positive and negative attitudes affect a person’s financial literacy. People will not be interested in learning about financial literacy, for example, if they have bad attitudes regarding saving money for the future. A survey revealed a constant favorable association between financial attitude and financial planning. People who practice good money management will have better financial circumstances, including higher savings and increased financial security for themselves and their families. Financial attitude is a vital formation that can enhance the savings intention of an individual as well as sustainable financial planning. Hassan et al. conducted a study in Malaysia and found that financial attitude positively relates to financial retirement planning. This study will propose the following hypothesis based on the above discussion:
H1: Financial attitude has a significant influence on financial retirement planning.
2.2. Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is described as possessing the necessary information and abilities to confidently make financial decisions and manage financial resources. Developing financial knowledge and skills and understanding the relationship between them are two parts of financial literacy that are based on people’s education or experience with financial concepts and goods. Financially literate people would know better than to spend more than their monthly income, which would leave them with ample savings when their income declines, especially after retirement. Moure examined the relationship between financial literacy and retirement planning in Chile and found a significant positive relationship between financial literacy and retirement planning. Studying the impact of financial literacy on retirement planning in sector work in Vietnam, Nguyen et al. came to similar conclusions. Based on the previous study results, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H2: Financial literacy has a significant influence on financial retirement planning.
2.3. Health Literacy
An individual’s attitude toward health, knowledge of their medical history and desire to make lifestyle changes are all part of their impression of their health status. One’s ability to earn money can be limited by ill health and disability. Malaysians continue to have low levels of general health literacy, according to the 2015 National and Morbidity Survey. Although it may accelerate a person’s decision to retire, poor health does not always impact retirement plans. Better financial literacy is linked to older people’s cognitive and mental health more so than higher health literacy, which stimulates regular physical activity. Since financial planning and health literacy are intertwined, a previous study hypothesizes that people who use health information search behavior are more likely to use retirement planning. Amoah looked into the connection between health literacy and wellbeing among rural and urban dwellers in Ghana and discovered that the two variables are positively correlated. A study by Wilson et al. looked at the impact of health literacy on older people’s cognitive health and found that higher health literacy was associated with decreased risk of developing incident Alzheimer’s disease. So, higher health literacy might result in high motivation to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Good financial retirement planning is needed to keep themselves healthy and have a good quality of life after retirement. Based on the reviews above, this study hypothesizes that:
H3 : Health literacy has a significant influence on financial retirement planning.
2.4. Role of a Financial Advisor
The best place to get specialized knowledge on financial planning is from financial advisors. A financial advisor’s responsibilities include coordinating, integrating and teaching their customers several aspects of financial planning, such as asset protection, retirement, debt management, tax and investment planning. A financial advisor needs to be qualified (for example, a certified financial planner), experienced and knowledgeable. Before being allowed to give investment advice in Malaysia, financial advisors must pass the necessary exams and have the necessary licenses from the Securities Commission (as well as the Central Bank of Malaysia, if they are insurance brokers). Financial advisors frequently assist clients with creating measurable goals, diversifying retirement accounts and improving their emergency preparedness from a retirement planning perspective. According to research, a person’s decision to seek professional guidance is influenced by financial attitude, expertise and demographic characteristics. People do not always use financial advisors; not all offer a high-quality, added-value advice. Thus, the financial advisor’s function may influence how well a person manages their behavior, giving them an edge or perceived behavioral control over their retirement savings decisions. Using a propensity score matching approach, Kim et al. looked at the connection between the function of a financial advisor and maintaining a retirement saving target and found that households that used a financial advisor were more likely than non-user households to cite retirement as the reason for saving. Rickwood et al. investigated the customer’s intention to save for retirement using a professional financial services advisor and the analysis indicated that the role of a professional financial services advisor did not directly influence the customers’ intention for retirement planning. According to Baron and Kenny, a variable can be used as moderating when the relationship between dependent and independent variables is not consistent. So, this study will utilize the role of the financial advisor as a moderating variable and proposes the below hypotheses:
H4: The role of the financial advisor moderates the relationship between financial attitude and financial retirement planning.
H5: The role of the financial advisor moderates the relationship between financial literacy and financial retirement planning.
H6: The role of the financial advisor moderates the relationship between health literacy and financial retirement planning.
Based on the discussion, it is evident that there is a research gap in using the role of the financial advisor as a moderating variable on the relationship between financial attitude, financial literacy, health literacy and financial retirement planning. So, this study proposes the below research framework in Figure 1.
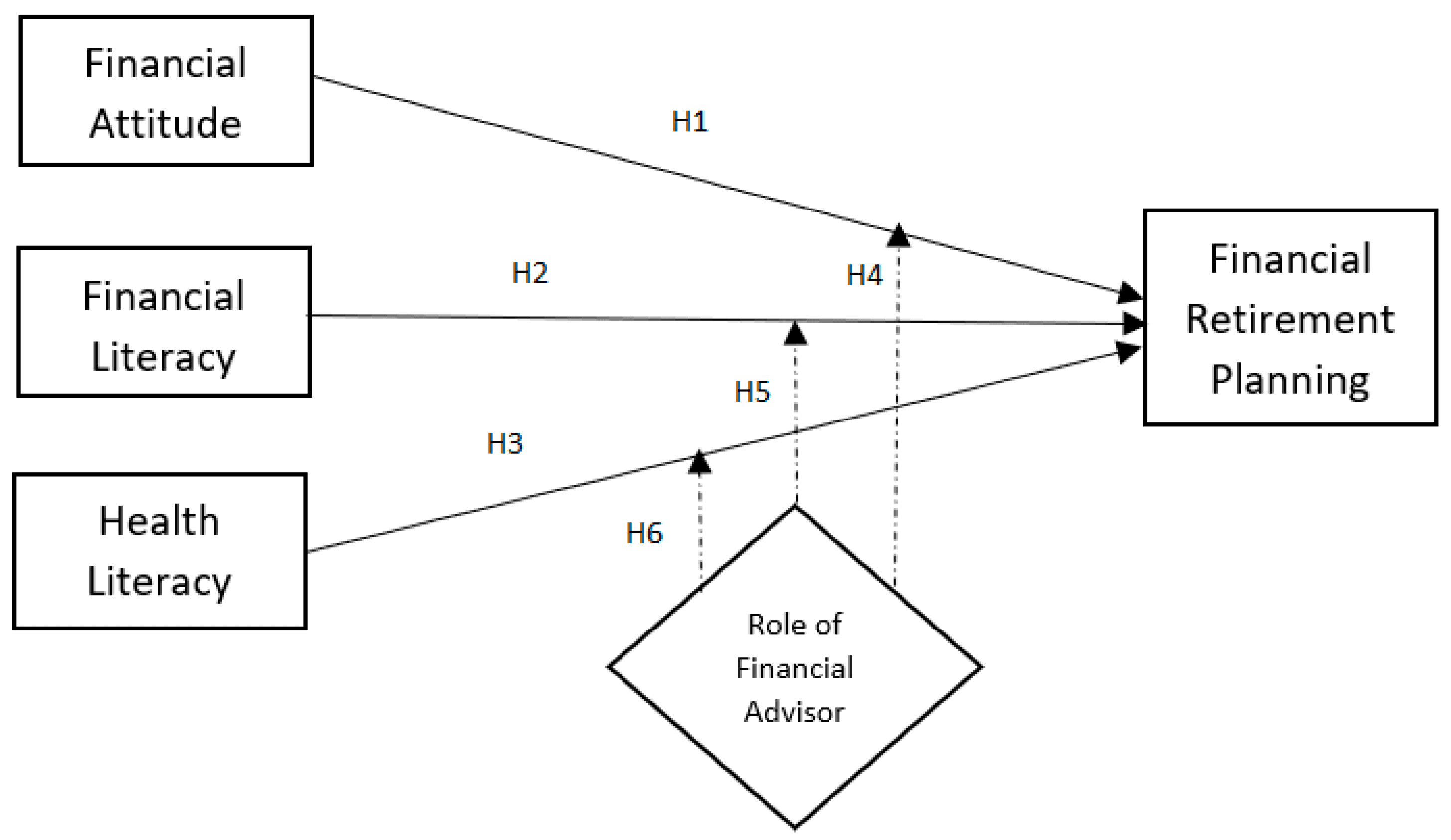
Figure 1. Research framework.
3. Methodology
A quantitative method was used to investigate the direct links between financial attitude, financial literacy, health literacy and financial retirement planning, as well as the moderating effect of a financial advisor on the relationships between the independent and dependent variables. This study aims to test the hypothesis developed to explore the effects of independent variables on the dependent variable and the moderating effect, which may strengthen the correlations. Typically, studies that test hypotheses explain the nature of definite correlations or establish the distinctions between groups or the independence of two or more components in a particular context. A cross-sectional design will be employed as the researcher plans to gather data just once.
Furthermore, the researcher collected data for this study through a questionnaire survey. This technique was used to obtain the respondents’ perceptions about the issue under consideration. To simplify the process of determining the sample size for a finite population, Sekaran and Bougie developed a table using a sample size formula for a given population for easy reference. The total population for the study was 645,136 small and medium-sized enterprises (SME). So, according to the table of Sekaran and Bougie, the sample size should be 383 SMEs. The unit of analysis for the current study is the individual owner of each SME. The response provided by the SME owner will represent him or herself as a self-employed individual. The study employed a five-point Likert scale to measure the instruments of measurement. The measurement instrument for financial retirement planning has been adapted from Selvadurai, V. In addition, the measurement instruments of financial attitude have been adapted from Mahlanza, T. J. (2015), of financial literacy from Fernandes et al. (2014), health literacy from Nga & Yeoh (2018) and the role of the financial advisor from Vlam (2011). The measurement items are available in the Appendix A section of the study.
A statistical method must be used to analyze the acquired data. Using the SmartPLS 3.0 M3 software, the data were also examined using the partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) technique. Most social sciences and management study fields use the partial least squares (PLS) path modelling. The estimation is being measured by researchers using the PLS-SEM approach. It has to do with how latent constructs and path models connect. There are two stages in the PLS-SEM analysis: the structural model and the measurement model.
4. Findings and Discussion
The summary of the respondents is given below in Table 1.
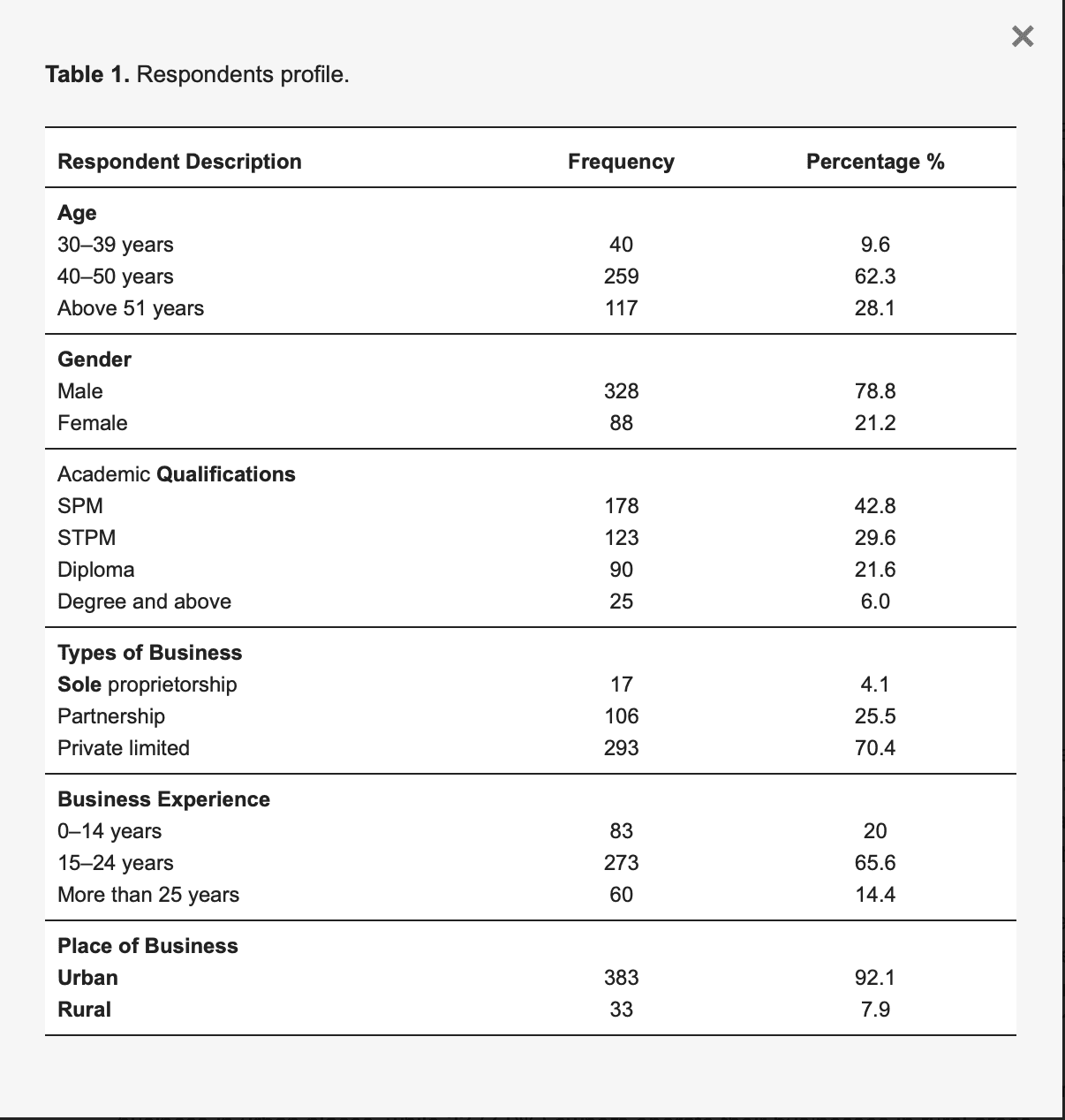
Table 1. Respondents profile.
Table 1 shows that 259 (62.3%) individual owners of the SMEs were aged between 40–50 years old, 117 (28.1%) were more than 51 years old and 40 (9.6%) were between 30–39 years old. The gender distribution of the SME owners consisted of 328 (78.8%) males, while the remaining 88 (21.2%) were female. In terms of academic qualifications, most of the respondents, 301 (72.4%), had finished secondary school, with 178 (42.8%) obtaining SPM certificates and 123 (29.6%) having STPM certificates. Other than that, 90 (21.6%) had diploma certificates, while 25 (6%) had an academic qualification of degree and above. It can also be observed from the table that individual SME owners have various types of businesses, such as owners with private limited businesses having the largest number 293 (70.4%), 106 (25.5%) partnership businesses and 17 (4.1%) sole proprietorship businesses. Table 1 further revealed that the highest number of SME owners, 273 (65.6%), have 15–24 years of business experience. In comparison, 83 (20%) have less than 15 years of business experience, and 60 (14.4%) of SME owners have more than 25 years of business experience. Moreover, 383 (92.1%) of most SMEs operate their business in urban places, while 33 (7.9%) owners operate their businesses in rural areas.
4.1. Assessment of Measurement Model
Assessment of the measurement model, also known as the outer model, is the initial step in the PLS analysis. Validity and reliability are the two most important criteria used in PLS analysis to evaluate measurement models. The results of item reliability, construct internal consistency reliability, convergent validity utilizing outer loading, composite reliability, average variance explained (AVE) and discriminant validity were derived from these two criteria of measurement model evaluation. According to Hair et al., the recommended value of each item’s loading must be greater than 0.708%. Regarding the previously indicated thresholds, items with loadings below 0.708% were eliminated. Based on the analysis, it was determined that HLIT03, FAD01, FAD07 and FAD15 had values of less than 0.7008. Therefore, these products were removed since they did not meet the criteria of a loading rate of at least 0.708%. Composite reliability (CR) estimates were utilized in this study to quantify internal consistency reliability. The CR coefficient should be at least 0.70. The preference for CR was based on its capacity to provide accurate estimates of a construct’s reliability by relaxing the incorrect assumption of tau equivalency (equal item component loading) in Cronbach alpha calculations. As expected, the coefficients of consistency reliability for all constructs in this investigation are higher than 0.7, showing that all constructs have appropriate internal consistency reliability. A variable is believed to have convergent validity when its components are converged or share a large proportion of variance. Consequently, average variance extracted (AVE) is the method most frequently employed by researchers to establish the convergent validity of a construct. To achieve sufficient convergent validity, the AVE of each latent variable must be more than 0.50, as stated by Chin (1998). All AVE values in this study exceeded the acceptable value of 0.50 for their respective variables, indicating sufficient convergent validity.
Table 2 shows the value of the loadings, CR and AVE.
CONSTRUCTS | ITEMS | LOADINGS | CR | AVE |
FINANCIAL ATTITUDE | FATT01 | 0.841 | ||
FATT02 | 0.847 | |||
FATT03 | 0.822 | |||
FATT04 | 0.812 | 0.852 | 0.763 | |
FATT05 | 0.735 | |||
FATT06 | 0.897 | |||
FATT07 | 0.768 | |||
FATT08 | 0.901 | |||
FINANCIAL LITERACY | FLIT01 | 0.878 | ||
FLIT02 | 0.803 | |||
FLIT03 | 0.839 | |||
FLIT04 | 0.767 | 0.876 | 0.726 | |
FLIT05 | 0.854 | |||
FLIT06 | 0.861 | |||
FLIT07 | 0.807 | |||
FLIT08 | 0.825 | |||
FINANCIAL RETIREMENT PLANNING | FRP01 | 0.825 | ||
FRP02 | 0.871 | |||
FRP03 | 0.853 | |||
FRP04 | 0.911 | 0.903 | 0.805 | |
FRP05 | 0.808 | |||
FRP06 | 0.812 | |||
FRP07 | 0.832 | |||
FRP08 | 0.922 | |||
HEALTH LITERACY | HLIT01 | 0.781 | ||
HLIT02 | 0.862 | |||
HLIT04 | 0.774 | |||
HLIT05 | 0.811 | 0.746 | 0.715 | |
HLIT06 | 0.849 | |||
HLIT07 | 0.881 | |||
HLIT08 | ||||
HLIT09 | 0.879 | 0.853 | ||
ROLE OF FINANCIAL ADVISOR | FAD02 | 0.819 | ||
FAD03 | 0.793 | |||
FAD04 | 0.821 | |||
FAD05 | 0.879 | |||
FAD06 | 0.754 | |||
FAD08 | 0.833 | |||
FAD09 | 0.865 | 0.878 | 0.726 | |
FAD10 | ||||
FAD11 | 0.844 | 0.881 | ||
FAD12 | ||||
FAD13 | 0.802 | 0.825 | ||
FAD14 | ||||
FAD16 | 0.855 | 0.872 |
Table 2. Loadings, CR and AVE values.
According to Hair et al., discriminant validity refers to how precisely one construct differs from another. Additionally, it is highlighted by the improbably low correlation between the relevant metrics and other measures that are not necessarily assessing the same thing. The method of addressing discriminant validity as the square root of each construct’s AVE compared to its correlations was described by Fornell and Larcker in 1981. According to Table 3, each construct’s computed square root of AVE was greater than the correlations between the constructs, which ensures appropriate discriminant validity.
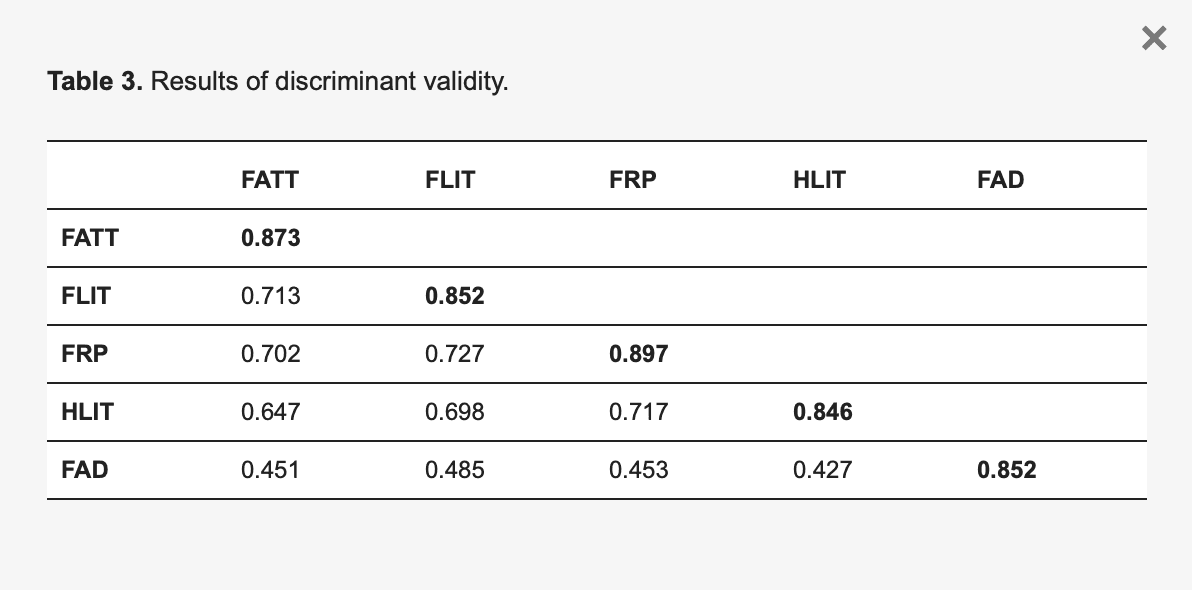
Table 3. Results of discriminant validity.
4.2. Assessment of Structural Model
The structural model evaluates the interactions between the endogenous variable, financial retirement planning, the moderator variable, the role of the financial advisor and the exogenous variables, financial attitude, health literacy and financial literacy.
According to the instructions of Hair et al., the structural model was evaluated in this work by first establishing the degree of collinearity between the set of constructs, then calculating the coefficient of variance explained (R2) and the importance of path coefficients.
According to Hair et al., looking at collinearity ensures that the structural model does not have problems with lateral collinearity. The collinearity analysis was made possible by calculating the variance inflation factor (VIF). The optimal range for the VIF values, according to Hair et al., is between 2.0 and 3.0. All the VIF values in Table 4 are below 3.0. This demonstrated that lateral multicollinearity is not a cause for concern.

Table 4. Values of VIF.
This study used bootstrapping to determine the statistical significance of the direct and indirect path coefficients. However, this work used a bootstrap sample of 5000, as advised by Hair et al., to estimate the direct path coefficients to ascertain the importance of the association between the variables in the structural models (2019). Table 5 displays the PLS structural model, with empirical t-values represented by the values inside brackets on the arrows and path coefficients represented by the values outside brackets, β.
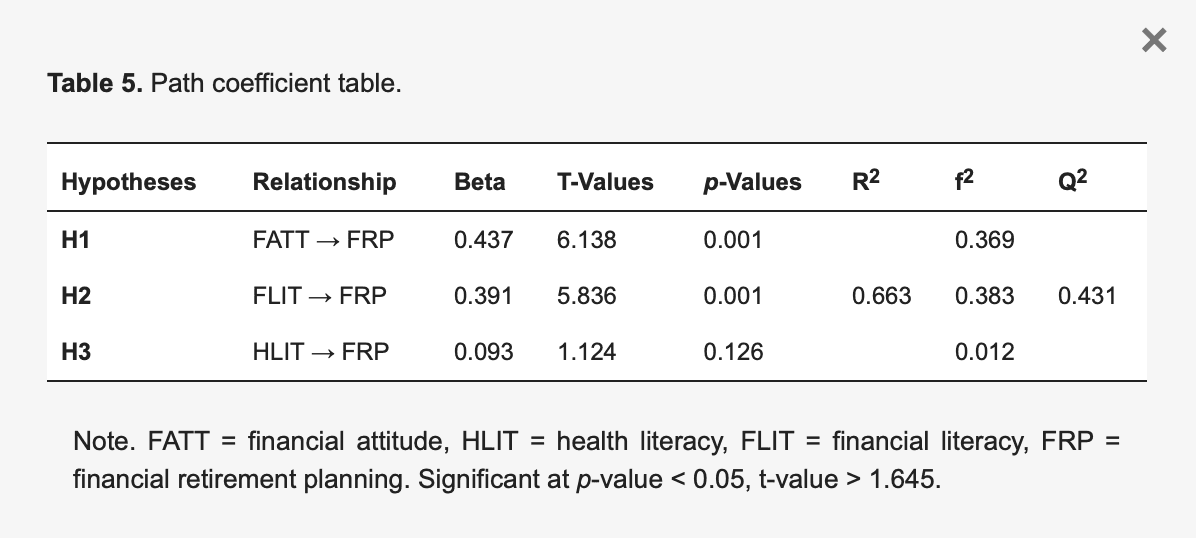
Table 5. Path coefficient table.
Table 5 indicates that two hypotheses are accepted as the value of p is less than 0.05. From the above table, it can be concluded that financial attitude and financial literacy positively influence financial retirement planning. However, financial attitude, health literacy and financial literacy are predictors of financial retirement planning, and together, they account for 66.3% of the variation in financial retirement planning. Both substantive significance (impact size) and statistical significance (p-value) must be reported when presenting a structural model. Three values of effect size—0.02 (little), 0.15 (mid) and 0.35 (large)—are explained by a Cohen (1988) guideline. Table 5, f2 value showed no effect for health literacy (0.012) because the effect size was less than 0.02. Still, there was a substantial effect size for financial attitude (0.369) and financial literacy (0.383). Q2 value is larger than 0, and then the model has a predictive relevance.
4.3. Moderating Path Coefficient Assessment
Moderation is used to condense or enhance the association between variables and influence the correlation’s strength or direction. Hair et al. recommended using a two-stage procedure in which the independent and moderating factors are evaluated. The goal is to discover whether the moderator has a substantial effect on the link between the independent and dependent variables, as in this study. As illustrated in Figure 2, the two-stage method was used to develop interactions between the moderator role of financial advisor (FAD) and three independent variables of the study: financial attitude (FATT), health literacy (HLIT) and financial literacy (FLIT). Figure 2 illustrates the PLS moderation model, with the values inside the brackets indicating empirical t-values and the values outside the brackets representing path coefficients, β.
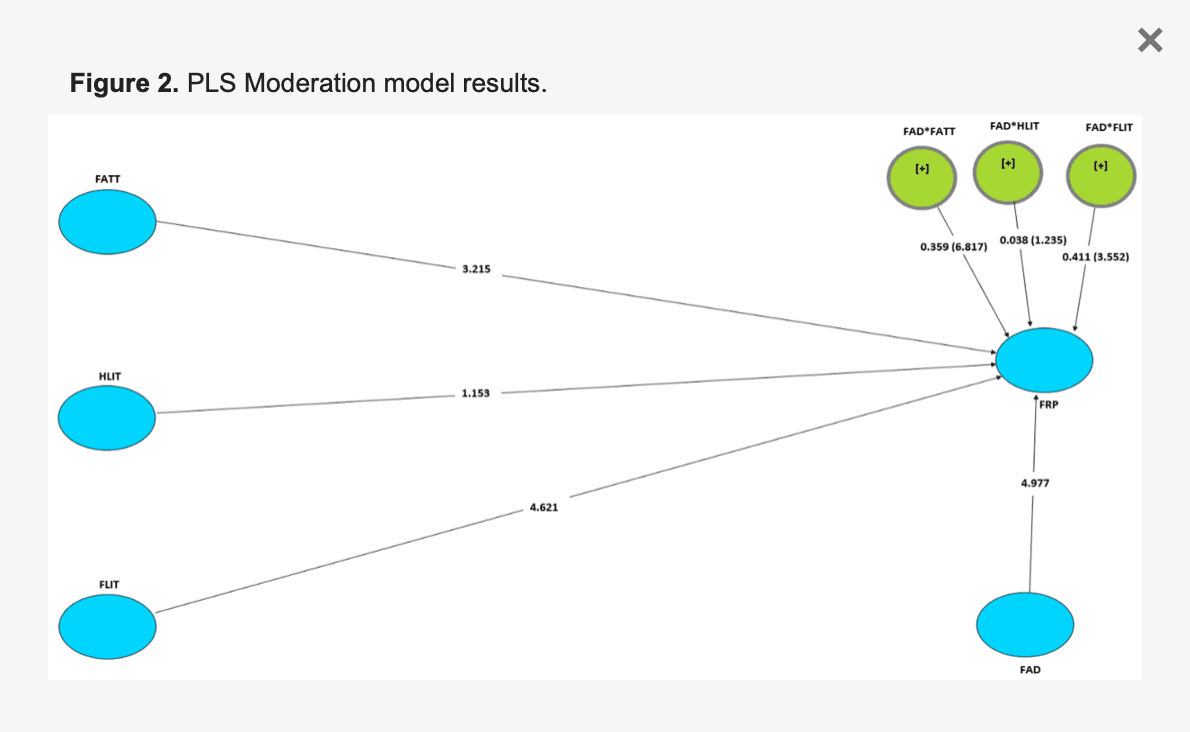
Figure 2. PLS Moderation model results.
Table 6 shows the outcome of the structural model for the moderating effects of the relationships between independent and dependent variables in this study.
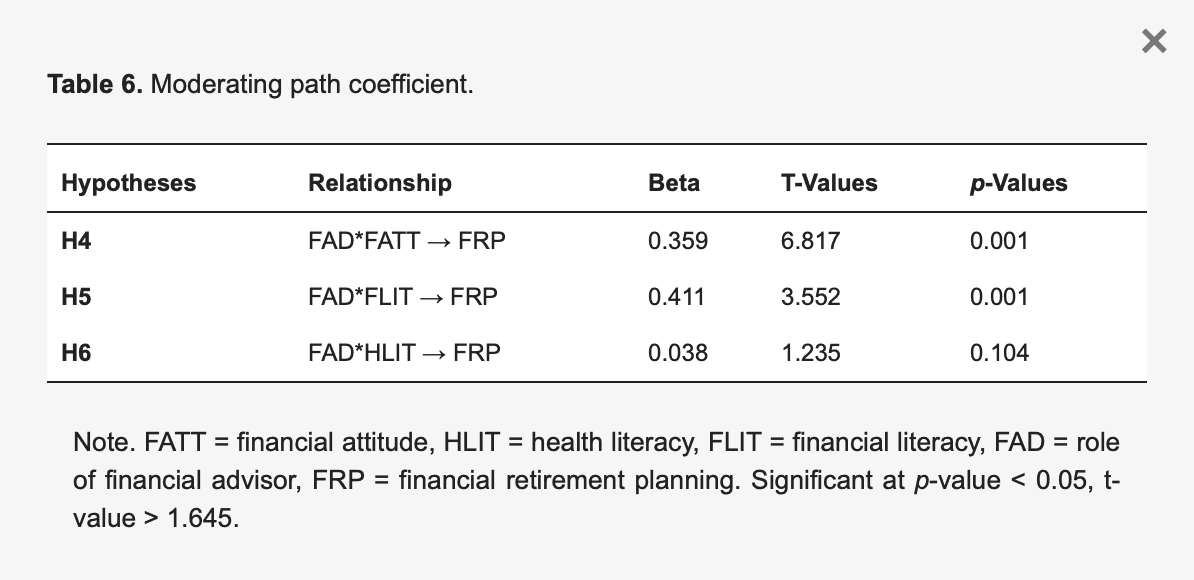
Table 6. Moderating path coefficient.
The moderating effect of the role of financial advisors on the connection between financial attitude and financial retirement planning is illustrated by FAD*FATT to FRP in Figure 2 and Table 6. The findings show that the position of financial advisor has a substantial moderating influence on the association between financial attitude and financial retirement planning (t = 6.817) and the p-value (p = 0.001). As a result, H4 is supported. Table 6 depicts the moderating influence of the function of a financial advisor on the association between financial literacy and financial retirement planning. The findings show that the function of a financial advisor has a substantial moderating influence on the connection between financial literacy and financial retirement planning (t = 6.817) and the p-value (p = 0.001). As a result, H5 is supported. The interaction path FAD*HLIT to FRP in Table 6 depicts the role of a financial advisor in moderating the association between health literacy and financial retirement planning. With t statistics (t = 1.235) and the p-value (p = 0.104), the interaction of the role of a financial advisor in the association between health literacy and financial retirement planning indicates a negligible impact, indicating that H6 is not supported.
Preacher et al. suggested that a simple two-way interaction slope be produced using the model’s path coefficients and interaction effects for hypotheses H4 and H5. The results are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively.
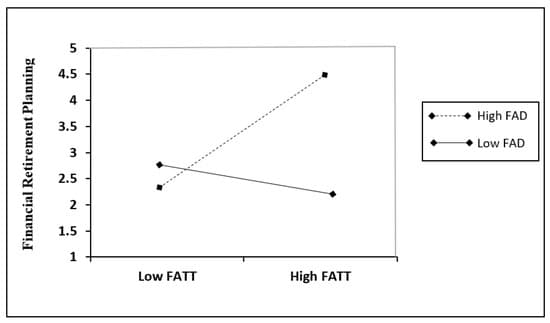
Figure 3. Interaction effect of FAD and FATT on FRP.
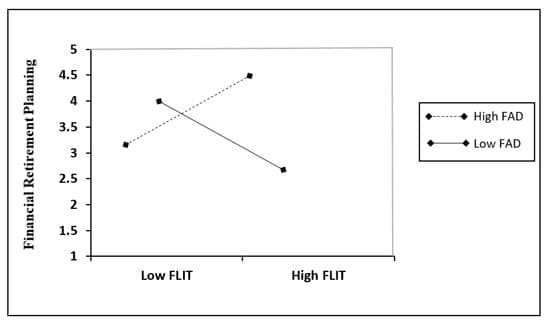
Figure 4. Interaction effect of FAD and FLIT on FRP.
Figure 3 represents the interaction effect of the role of a financial advisor (FAD) and financial attitude (FATT) on financial retirement planning (FRP). As observed from Figure 3, hypothesis H4 on the moderating effect of FAD on the relationship between FATT and FRP, the positive relationship between FATT and FRP is strengthened in the case of a high level of FAD, while with a low level of FAD, the relationship between FATT and FRP is weakened. This means that the bigger the role of financial advisors in influencing SME owners to have good retirement planning, the stronger the positive relationship between FATT and FRP, and vice versa.
According to Figure 4, hypothesis H5 on the moderating influence of FAD on the relationship between FLIT and FRP, a high level of FAD strengthens the positive association between FLIT and FRP, whereas a low level of FAD weakens the relationship between FLIT and FRP. This suggests that the greater the importance of financial advisors in persuading SME owners to plan for retirement, the larger the favorable association between FLIT and FRP, and vice versa.
4.4. Discussion
Financial planning is vital for the future before retirement. Retirement will be a nightmare if proper planning is not implemented, especially if retirees face economic difficulties once they retire. Persons who did not plan for retirement would need to work even after retirement to cover their living expenditures. Proper financial planning is vital for a happy retirement lifestyle and for ensuring financial stability for retirees and their families. Individuals with higher levels of income and education are more likely to plan for retirement by saving a larger proportion of their income. Factors such as supporting direct and indirect dependency influenced attitudes toward financial management. When people understand they must financially support their families, they learn financial discipline. Cabler said that people who practiced financial discipline had a better financial status, such as higher savings and greater financial security for themselves and their families.
The result revealed that financial attitude has a strong positive impact on financial retirement planning. The result is consistent with the previous study. Having a financial attitude can make an individual aware of their current financial situation, which is essential when planning for retirement. Tracking monthly expenditures might help individuals save money and prevent unnecessary splurging, which is vital for appropriate retirement financial planning.
Furthermore, the study found that financial literacy has a considerably positive impact on financial retirement planning. Financial literacy is vital for retirement planning. The result is consistent with earlier studies. Individuals with solid financial literacy have the required skills and knowledge to make sound and impactful retirement planning decisions with all their incomes and assets, such as creating additional income and increasing personal savings. According to Lusardi and Mitchell, individuals with relevant financial literacy have the skills, information and wisdom to spend their income wisely and save enough for retirement. On the same theme, an OECD (2013) report indicated that people must be financially educated to make sound saving decisions. Hung et al. discovered that, with relevant financial literacy, economic and financial decisions could be made more confidently, and financial resources could be handled successfully. However, health literacy showed no impact on financial retirement planning. The result is not consistent with earlier studies.
The study results revealed that the role of a financial advisor moderates the relationship between financial attitude and financial literacy in financial retirement planning. According to the findings of this study, a person’s financial knowledge and attitudes can support positive retirement financial planning. Furthermore, the significant moderating effect of the agents’ financial advisory role revealed that when consumers encounter financial problems and concerns, those who actively seek advice are significantly associated with better retirement financial planning because agents could help their consumers gain knowledge while promoting positive financial behavior and financial wellness. Financial planners, for example, could provide advice that leads to informed decision-making and improved financial outcomes, allowing their customers to become more conscious of the importance of retirement savings. Financial planners, for example, could assist their clients in planning for retirement by becoming essential information sources and providing valuable services to consumers, such as reducing overall wealth volatility, assisting clients in increasing their wealth, preventing financial losses and smoothing lifetime consumption levels. Furthermore, long-term interaction with financial planning professionals can improve consumers’ financial condition and different elements of well-being, as well as increase their financial regulatory understanding and experience. This study underlined the significance of agents such as financial planners as key financial information sources, as they positively influenced consumers’ financial actions in retirement planning. Since this study discovered that the role of agents in retirement planning significantly moderated financial literacy and financial attitude, there are opportunities for agents such as financial advisors and planners to explore and implement client communication strategies into their best practices to help build consumers’ knowledge and confidence, which can be useful for better management of their financial issues. As a result, officials at the state and federal levels should make professional financial services more accessible and cheaper to the general population, particularly self-employed individuals. The aims of boosting financial literacy and financial attitude are critical since low financial literacy and attitude can lead to harmful financial behaviors, such as failing to plan for retirement.
5. Conclusions
One of the most important stages of life is retirement. After a long period of hard work, people now cease working and take time to relax at home. A pleasant retirement requires careful planning. In retirement, financial assistance is vital. Thus, one of the most important aspects of retirement is financial planning. Those who do not save their funds for retirement may experience financial hardship when faced with unforeseen circumstances, such as having to pay for high medical costs. As people age, situations like these are more likely to occur. Therefore, effective retirement financial planning is crucial for overcoming unanticipated events. Finding the important factors influencing Malaysian self-employed people’s financial retirement planning is the main goal of this study. The study’s final output is the conceptual model describing financial retirement planning among self-employed people. The self-administered questionnaires were given to the study’s participants as part of the quantitative research strategy used to carry out this study. The goal was to pinpoint the important variables affecting Malaysian independent professionals’ financial retirement planning. The study’s results showed a substantial direct association between the dependent variable, financial retirement planning and two independent factors, namely financial attitude and financial literacy. Furthermore, no association between the independent variable’s financial retirement planning and health literacy was discovered. In addition, the financial advisor’s function considerably moderates the association between financial attitude and financial literacy toward financial retirement planning. These findings can be helpful for those keen to know the essential determinants that affect sustainable financial planning for retirement among self-employed individuals in Malaysia.
5.1. Managerial Implications
The study’s findings have various implications for future retirees, younger generations and politicians. Policymakers should raise financial retirement planning awareness among all self-employed individuals, regardless of socioeconomic background. Furthermore, self-employed people might apply some of the concepts explored in this study to plan their retirement. The study’s findings may also impact the younger generation, who know that even with a guaranteed income, saving money will be difficult given the rising cost of goods and services. This study contributed to developing a conceptual framework for financial retirement planning among Malaysian independent contractors. It is designed to suit the needs of self-employed individuals preparing for retirement by covering the variables necessary for solid financial planning.
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
This study has several drawbacks. The presence of a sample representative of Malaysia’s self-employed population. The samples in this study are mostly from Malaysia’s northern states. Furthermore, obtaining the equivalent number of samples from Malay, Chinese and Indian ethnicities is problematic. Most of the samples are from the Malay community. Their cultural upbringing would influence their views on financial literacy and planning. Psychological variables such as goal setting, exposure and awareness can be included by future researchers. These criteria are important elements to consider when planning for retirement.